The Custom HTML block in WordPress allows you to insert and edit HTML code directly within your content in the Gutenberg editor. It’s a versatile block that you can use for various purposes, like adding ads, maps, videos, iframes, tables, and more.
You can also use it to markup your text and then convert it to a Paragraph Block. In this article, I will explain step-by-step how to add and use the WordPress HTML block.
Step 01: Search the Custom HTML Block
Like any other block, search the Custom HTML block in the Gutenberg block library. Hit the plus (+) button on the editor. Type Custom HTML in the search bar. The block will appear in a second. Click and add it to the editor.
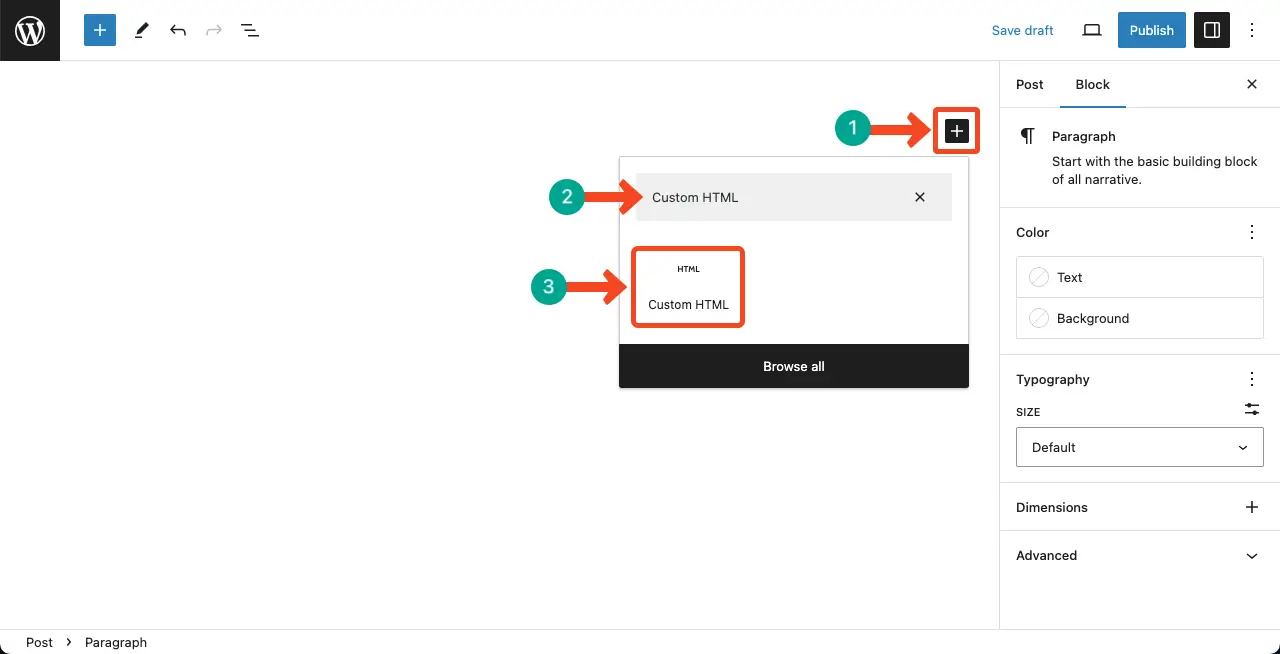
The Custom HTML block will be added to the editor instantly. You can see it in the image below.
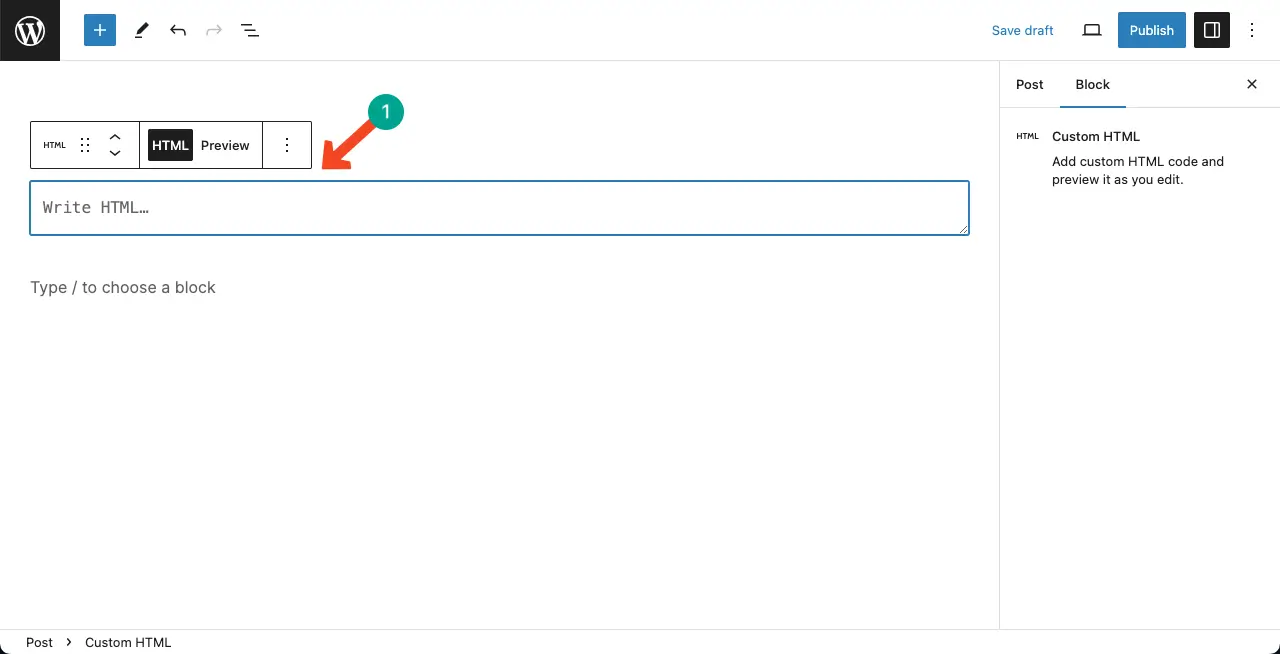
Step 02: Add HTML Code to the Custom HTML Block
It’s simple. Just copy-paste the HTML code to the block. Here for the tutorial, I have copy-pasted an HTML code from the Google Map.
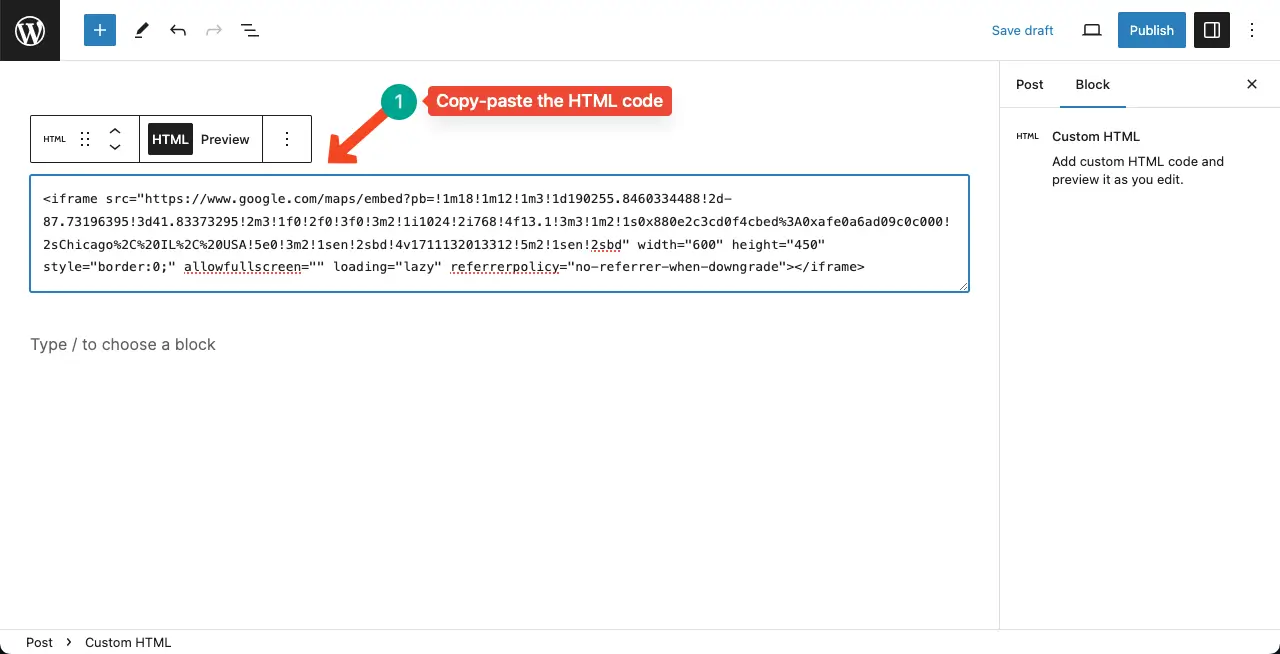
Step 03: Preview the Visual of the Custom HTML Code
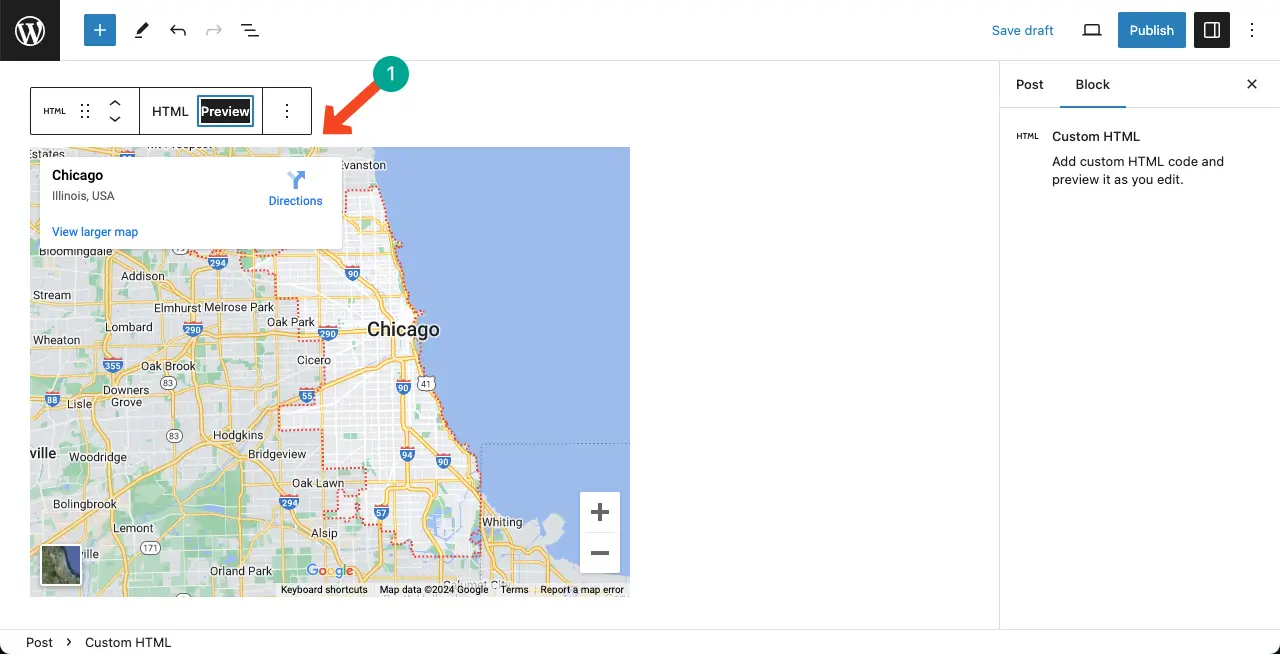
Before publishing the content, you may want to preview it. So, click the Preview option on the Gutenberg toolbar. You’ll see the visual.
You can see the Google Map in the image below whose code we have added to the block. Next, you can publish the content.
Tags that the WordPress Custom HTML Block Supports
WordPress.com allows you to use the following HTML tags on the editor.
- a
- address
- abbr
- acronym
- area
- article
- aside
- b
- big
- blockquote
- br
- caption
- cite
- class
- code
- col
- del
- details
- dd
- div
- dl
- dt
- em
- figure
- figcaption
- footer
- font
- h1, h2, … h6
- header
- hgroup
- i
- img
- ins
- kbd
- il
- map
- mark
- ol
- p
- pre
- q
- rp
- rt
- rtc
- ruby
- s
- section
- small
- span
- strike
- strong
- sub
- summary
- sup
- table
- tbody
- td
- tfoot
- th
- thread
- tr
- tt
- u
- ul
- var
Note: WordPress doesn’t allow all the HTML tags in its Custom HTML block for security reasons. If there is any tag that the block doesn’t support, you have to use additional plugins for them.
Best Practices for Using the Custom HTML Block
Use the Custom HTML block for specific purposes: The Custom HTML block is great for embedding certain types of code, such as Google Maps, videos, iframes, and more. It is also useful for marking up your text and then converting it to a Paragraph Block with styled text if desired.
Be mindful of security: Not all HTML tags are allowed in the Custom HTML block for security reasons. It’s important to check the list of supported HTML tags to ensure you are using the ones that are allowed.
Preview and test your code: The Custom HTML block allows you to preview the added HTML code. Take advantage of this feature to ensure that your code is rendering correctly. Additionally, it’s a good practice to test your code across different devices and browsers to ensure compatibility.
Use external files for CSS and JS: Instead of including CSS and JS code directly within the Custom HTML block, it’s a good practice to place them in external files. This allows for better organization, reusability, and maintainability of your code.
Conclusion
Thus, you can use the Custom HTML block in WordPress. Also, by following the guidelines stated above, you can make the most of the block and enjoy endless possibilities for showcasing HTML content on your website. Take a look at how to use the Gutenberg Paragraph block in WordPress.
